5.4 Thermal
Properties
5.4.1 Thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity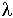 [Wm^-1 K^-1] of ceramics is generally less than that
of metals such as steel or copper. Materials such as silicon
carbide or aluminium nitride however, find applications as
heat conductors, due to their relatively high thermal conductivity
compared with other electrically insulating materials.
[Wm^-1 K^-1] of ceramics is generally less than that
of metals such as steel or copper. Materials such as silicon
carbide or aluminium nitride however, find applications as
heat conductors, due to their relatively high thermal conductivity
compared with other electrically insulating materials.
Other ceramic materials, in contrast, are used for thermal
insulation due to their low thermal conductivity. These insulating
properties can be enhanced by inducing porosity in the ceramic.
Ceramic fibre matting has a similar effect.
When comparing the thermal conductivity of different materials,
it is important to note the temperature range, e.g. 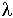 30-100
for figures relevant to the range from 30 to 100 °C. 30-100
for figures relevant to the range from 30 to 100 °C.
Test procedures for determining thermal diffusivity (a), which
is related to thermal conductivity as ?= a·?·cp,
are specified in DIN EN 821-2.

Figure 90: A guide to the flexural strength
and thermal conductivity of selected materials

Figure 91: A guide to the coefficient of
thermal expansion and thermal conductivity of selected materials
|
|

