4.1.6 Machining
As shown in figure 62, green machining
(after drying), white machining (after burning
out and prefiring) and hard machining (after
sintering) are to be distinguished.
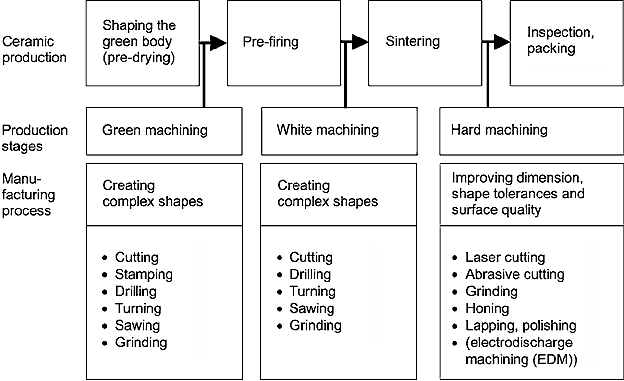
Figure 62: Classification of green, white
and hard machining in the production process
Green machining
is performed on the dry parts while they still contain organic
additives. It is well suited to the manufacture of individual
parts and small series. It is also used with large series
to manufacture shapes that cannot be realised directly by
initial forming procedure, such as holes transverse to the
direction of dry pressing.
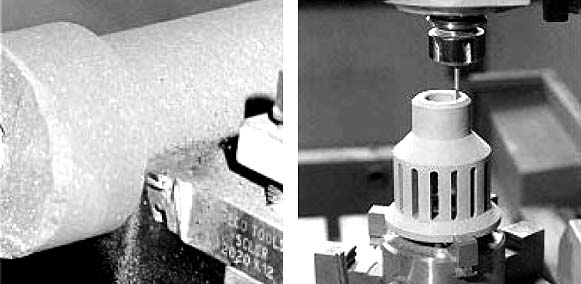
Figures 63 and 64: Components being machined
green
White machining
is performed on the prefired parts, now free from organic
additives. The strength depends on the prefiring.
In this way, extremely high removal rates be achieved with
relatively low tool wear using conventional, ceramic or diamond
coated tools. This process is used by manufacturers both for
making prototypes and for mass production.
|

